1. Phạm vi áp dụng:
Tiêu chuẩn này qui định các thuật ngữ và định nghĩa chính liên quan đến gạo
Tiêu chuẩn bao gồm các phần: khái niệm chung, kích thước, mức xát và chỉ tiêu chất lượng của gạo.
|
Thuật ngữ
|
Định nghĩa
|
|
2. Khái niệm chung
General conception
2.1. Thóc
Paddy
2.2. Gạo
Rice
2.3. Gạo lật (gạo lứt)
Husked rice (milled
rice, cargo rice)
2.4. Gạo trắng (gạo xát)
White rice (milled rice)
2.5. Gạo nếp
Glutinous rice (waxy rice)
2.6. Gạo thơm
Aromatic
2.7. Gạo đồ
Parboiled rice
2.8. Gạo mốc
Muddy rice
2.9. Gạo bẩn
Dirty apparent rice
2.10. Chuyến hàng
Consignment
2.11. Lô hàng
Lot
2.12. Mẫu – Sample
2.13. Mẫu ban đầu(mẫu điểm)
Increment
2.14. Mẫu riêng
Separate sample
2.15. Mẫu chung(mẫu gốc)
Bulk sample
2.16. Mẫu trung bình
Laboratory sample
2.17. Mẫu phân tích
Analysis sample
3. Kích thước hạt gạo
Size of rice kernel
3.1. Kích thước hạt gạo
Size of rice kernel
3.2. Chiều dài trung bình của hạt
Average length of rice kernel
3.3. Phân loại hạt
Classification of kernels
3.3.1. Hạt rất dài
Very long kernel
3.3.2. Hạt dài-long kernel
3.3.3. Hạt ngắn-short kernel
4. Mức xát của gạo
Milling degree of rice
4.1. Gạo xát rất kỹ
Extra-well-milled rice
4.2. Gạo xát kỹ
Well-milled rice
4.3. Gạo xát vừa phải
Reasonable milled rice
4.4. Gạo xát bình thường
Ordinary-milled rice
5. Chỉ tiêu chất lượng của gạo
Quality factors of rice
5.1. Độ ẩm
Moisture
5.2. Tạp chất
Impurities (foreign matters),
extraneous matters
5.2.1. Tạp chất vô cơ
Inorganic impurities
5.2.2. Tạp chất hữu cơ
Organic impurities
5.3. Hạt nguyên
Whole kernel
5.4. Gạo nguyên (hạt mẻ đầu)
Head rice
5.5. Tấm
Broken kernel
5.5.1. Tấm lớn
Big broken kernel, large
broken kernel
5.5.2. Tấm trung bình
Medium broken kernel
5.6. Tấm nhỏ
Small broken kernel
5.7. Tấm mẳn
Chip
5.8. Hạt lẫn loại
Other types (Contrasting
classes, admixture)
5.9. Hạt vàng
Yellow kernel
5.10. Hạt bạc phấn
Chalky kernel
5.11. Hạt bị hư hỏng
Damaged kernel
5.12. Hạt bị hư hỏng do nhiệt
(áp dụng cho gạo đồ)
Heat damaged kernel
5.13. Hạt xanh non
Green kernel (immature
kernel and malformed
kernel)
5.14. Hạt đỏ
Red kernel
5.15. Hạt sọc đỏ
Red streaked kernel
5.16. Hạt gạo xát dối
Undermilled rice kernel
5.17. Mùi vị lạ
Commercially objectionable
foreign odours
5.18. Gạo không có sâu mọt
Insect free rice
5.19. Gạo nhiễm sâu mọt
Infected rice
5.20. Dư lượng hóa chất
Chemical residue
|
Hạt lúa chưa được bóc vỏ trấu
Phần còn lại của hạt thóc thuộc các giống lúa (Oryza sativa.L) sau khi đã tách bỏ hết vỏ trấu, tách một phần hay toàn bộ cám và phôi
Phần còn lại của thóc sau khi đã tách bỏ hết vỏ trấu
Phần còn lại của gạo lật sau khi đã tách bỏ một phần hoặc toàn bộ cám và phôi
Gạo thuộc giống lúa Oryza sativa.L glutinoza có nôi nhũ trắng đục hoàn toàn: có mùi, vị đặc trưng, khi nấu chín, hạt cơm dẻo, dính với nhau có màu trắng trong; thành phần tinh bột hầu hết là amylopectin
Gạo có hương thơm đặc trưng
Gạo được chế biến từ thóc đồ, gạo lật đồ, do đó tinh bột được hô hóa hoàn toàn, sau đó được sấy khô.
Gạo bị nhiễm nấm mốc, có thể đánh giá được bằng cảm quan
Gạo bị mất màu trắng tự nhiên do các chất dính trên bề mặt hạt
Một khối lượng gạo nhất định được xuất đi hoặc nhập về một lần, theo một hợp đồng nhất định hoặc theo hóa đơn xuất hàng. Chuyến hàng có một hoặc nhiều lô hàng
Khối lượng gạo xác định có cùng chất lượng, là một phần của chuyến hàng và được phép lấy mẫu để đánh giá chất lượng
Khối lượng gạo của lô hàng được lấy ra theo một qui tắc nhất định
Khối lượng gạo nhất định được lấy từ một vị trí trong lô
Gộp các mẫu ban đầu của một đơn vị bao gói
Gộp các mẫu riêng hoặc mẫu ban đầu
Khối lượng gạo nhất định được thành lập từ mẫu chung theo một qui tắc nhất định, dùng để làm mẫu lưu và mẫu phân tích
Khối lượng gạo được dùng trong phép phân tích
Chiều dài và chiều rộng của hạt gạo không bị gãy vỡ tính bằng milimét
Chiều dài trung bình của hạt được xác định bằng cách tính trung bính cộng chiều dài của 100 hạt gạo không gãy vỡ được lấy ngẫu nhiên từ mẫu gạo thí nghiệm.
Gạo được phân theo chiều dài của hạt
Hạt có chiều dài lớn hơn 7mm
Hạt có chiều dài từ 6mm đến 7mm
Hạt có chiều dài nhỏ hơn 6mm
Mức độ tách bỏ phôi và các lớp cám trên bề mặt hạt gạo
Gạo lật được loại bỏ hoàn toàn các lớp cám và phôi và một phần nôi nhũ
Gạo lật được loại bỏ hoàn toàn phôi, các lớp cám ngoài và phần lớn lớp cám trong
Gạo lật được loại bỏ phần lớn phôi và các lớp cám
Gạo lật được loại bỏ một phần phôi và các lớp cám
Lượng nước tự do của hạt, được xác định bằng phần trăm khối lượng bị mất đi trong quá trình sấy mẫu ở nhiệt độ 1050C đến khối lượng không đổi
Những vật chất không phải là gạo và thóc
Mảnh đá, kim loại, đất, gạch và tro bụi... lẫn trong gạo
Hạt cỏ dại, trấu, cám, mảnh rơm, rác, xác sâu, mọt... lẫn trong gạo
Hạt gạo không gãy vỡ và hạt có chiều dài bằng hoặc lớn hơn 9/10 chiều dài trung bình của hạt gạo
Bao gồm các hạt gạo có chiều dài lớn hơn 8/10 chiều dài trung bình của hạt gạo
Hạt gạo gãy có chiều dài từ 2,5/10 đến 8/10 chiều dài trung bình của hạt gạo nhưng không lọt qua sàn ö 1,4mm, và tùy từng loại gạo sẽ được qui định kích cỡ tấm phù hợp
Hạt gạo gẫy có chiều dài lớn hơn 5/10 đến 8/10 chiều dài trung bình của hạt gạo
Hạt gạo gẫy có chiều dài từ 2,5/10 đến 5/10 chiều dài trung bình của hạt gạo
Phần hạt gẫy có chiều dài nhỏ hơn 2,5/10 chiều dài của hạt gạo, lọt qua sàng ö 2mm nhưng không lọt qua sàng ö 1,4mm
Những mảnh gẫy, vỡ lọt qua sàng ö 1,4mm và không lọt qua sàng ö 1,0mm
Những hạt gạo khác giống, có kích thước và hình dạng khác với hạt gạo theo yêu cầu
Hạt gạo có một phần hoặc toàn bộ nôi nhũ biến đổi sang màu vàng rõ rệt
Hạt gạo (trừ gạo nếp) có ¾ diện tích bề mặt hạt trở lên có màu trắng đục như phấn
Hạt gạo bị giảm chất lượng rõ rệt do ẩm, sâu bệnh, nấm mốc, côn trùng phá hoại và/hoặc do nguyên nhân khác
Hạt gạo bị thay đổi màu tự nhiên do nhiệt sinh ra vì hoạt động của vi sinh vật, do quá trình sinh hóa của hạt, do sấy qua lửa
Hạt gạo từ hạt lúa chưa chín và/hoặc phát triển chưa đầy đủ
Hạt gạo có lớp cám màu đỏ lớn hơn hoặc bằng ¼ diện tích bề mặt của hạt
Hạt gạo có một sọc đỏ mà chiều dài bằng hoặc lớn hơn ½ chiều dài của hạt, hoặc tổng chiều dài của các vệt sọc đỏ lớn hơn ½ chiều dài của hạt, nhưng tổng diện tích của các sọc đỏ nhỏ hơn ¼ diện tích bề mặt của hạt
Hạt gạo còn lớp cám lớn hơn ¼ diện tích bề mặt của hạt hoặc còn những vết cám mà tổng chiều dài của nó bằng hoặc lớn hơn chiều dài của hạt
Không phải mùi, vị đặc trưng của gạo
Gạo không có sâu mọt sống và có không quá 5 con sâu mọt chết trên 1 kg gạo
Gạo có không quá 5 con sâu mọt sống trên 1 kg gạo, trong đó không có loại mọt sitophilus granarius
Lượng hóa chất tồn dư có trong gạo
|
Rice-Terms and Definitions
1. Scope of applications
This standard lays down general terms and definitions in relation to rice
It includes the following parts: general conception, size, milling degree, and quality factors of rice
2. General conception
2.1. Paddy: rough rice has retained its husk after threshing
2.2. Rice: paddy from which the husk, all or a part of bran, and the embryo, has been removed
2.3. Husked rice: paddy from which only the husk has been removed
2.4. White rice: Husked rice, from which all or part of the bran, and the embryo, has been removed
2.5. Glutinous rice, waxy rice, (Oryza sativa.L glutinosa): rice, the kernels of which have a white and opaque appearance
The colour and aroma of it are special. The starch of waxy rice consists mainly of amylopectin; after cooking, the kernel shaves have a tendency to stick together
2.6. Aromatic rice: Rice has an aromatic fragrance
2.7. Parboiled rice: Rice obtained from paddy or husked rice that has been soaked in water and subjected to a heat treatment so that the starch is fully gelatinised and followed by a drying process
2.8. Muddy rice: Rice contaminated by mould that can bee seen with the naked eye
2.9. Dirty apparent rice: Rice which has had its natural colour changed by attached foreign matter on the surface of the kernels
2.10. Consigment: certain amounts of rice received or despatched at one time covered by a particular contract or shipping document. Consigment may consist of one or more lots
2.11. Lot: certain amounts of rice of the same quality, the same name or same code, packed in the same kind of packages and delivered at the same time
2.12. Sample: An amount of rice drawn by a specified rule
2.13. Increment (primary sample): The amount of rice drawn from one point or a single container
2.14. Separate sample: Mixing all primary samples drawn from different positions of one package
2.15. Bulk samples: The sample obtained by bringing together and mixing the primary sample or separate sample
2.16. Laboratory sample: Prescribed quantity drawn from the bulk sample, representative of the lot, and intended for analysis or other examinations
2.17. Analytical sample: The sample drawn from a laboratory sample and intended for the examination
3. Size of rice kernel
3.1. Size of rice kernel: The length and the width of the unbroken rice kernel in mm
3.2. Average length of rice kernel: value obtained by calculating the arithmetic mean length of 100 unbroken kernels from a laboratory sample
3.3. Classification of kernels: Classes of rice based on the length of rice kernels
3.3.1. Very long kernel: Whole kernel that has a length exceeding 7.0 mm
3.3.2. Long kernel: Whole kernel that has a length more than, or equal to 6.0 mm, but less than or equal to 7.0 mm
3.3.3. Short kernel: Whole kernel that has a length of less than 6.0 mm
4. Milling degree of rice:
Removal degree of bran and embryo of rice
4.1. Extra-well milled: Rice obtained by milling husked rice in such a way that all layers of the bran, embryo and part of the germ have been removed
4.2. Well-milled: Rice obtained by milling husked rice in such a way that all external bran, germ and most of the internal bran has been removed
4.3. Reasonably milled: Rice obtained by milling husked rice in such a way that most of the germ and the bran have been removed
4.4. Ordinary-milled: Rice obtained by milling husked rice in such a way that a part of the bran and the embryo have been removed
5. Quality factors to rice:
5.1. Moisture: The loss of mass by heating rice at 1050C until the mass of sample reaches constancy
5.2. Impurities: (foreign matter) All the substances other than kernels of rice
5.2.1. Inorganic impurities: Fragments of stone, sand, bran, and insects, etc.
5.2.2. Organic impurities: Foreign seed, husk, bran, and insects, etc.
5.3. Whole kernel: An unbroken kernel and broken kernel, the length of which is greater than, or equal to 9/10 of the average length of a kernel(2.2)
5.4. Head rice: The whole kernel or part of kernel, the length of which is greater than 8/10 of the average length of a kernel
5.5. Broken kernel: The part of the kernel the length of which is equal to, or greater than 2,5/10 but less than, or equal to, 8/10 of the average length of a kernel and does not pass through a mental sieve with a perforation ö 1,4mm, and the size of a broken kernel to be determined by each grade of rice
5.5.1. Large broken kernel: The part of a kernel the length of which is equal to or greater than 5/10 but less than, or equal to, 8/10 of the average length of a kernel
5.5.2. Medium broken kernel: The part of a kernel the length of which is equal to, or greater than, 2,5/10 but less than or equal to 5/10 of the average length of a kernel
5.6. Small broken kernel: The part of a broken the length of which is less than 2.5/10 of the average length of a kernel that can pass through a mental sieve with perforation ö 2.0mm but does not pass through a mental sieve with a perforation ö 1,4mm
5.7. Chip: Fragments of a kernel, which pass through a mental sieve with perforation of ö 1,4mm but do not pass through a mental sieve with a perforation of ö 1,0mm
5.8. Other types of rice: (admixture) Rice kernels the size and shape of which are different from destination rice kernel
5.9. Yellow kernel: Rice kernels that have a part, or all part, that turn to a visible yellow colour
5.10. Chalky kernel: Rice kernels (except for waxy rice) whole or ¾ surface of which has an opaque and floury appearance
5.11. Damaged kernel: Rice kernels the quality of which were reduced obviously due to moisture, fungi, insect and other causes
5.12. Heat damaged kernel: (Using for parboiled rice): Rice kernels the natural colour of which have changed as a result of a microbiological activity, biochemical reaction, and/or due to overheating
5.13. Immature and malformed kernel: Rice kernels are unrice and/or badly developed
5.14. Red kernel: Rice kernel having a red colour covering more than one-quarter of its surface
5.15. Red streaked kernel: Rice kernel with red streaks, the length of which is greater than, or equal to, one-half of the length of kernel; but the surface covered by these red streaks is less than one-quarter of the whole surface of kernel
5.16. Undermilled rice kernel: Rice kernels covered by bran streaks, the length of which is greater than or equal to the length of the kernel or the surface of bran streaks is greater than one-quarter of the surface of the kernel
5.17. Foreign odour: Not the natural aroma of rice
5.18. Insect free-rice: Rice free from living insects, and less than five dead insects per kg
5.19. Insected rice: Rice in which there are less than, or equal to, five living insects per kg but which should be free of sitophilus granarius
5.20. Chemical residue: Residues of chemicals in rice
Gạo trắng-yêu cầu kỹ thuật
White rice-Specifications
1. Phạm vi áp dụng
Tiêu chuẩn này áp dụng cho các loại gạo thuộc giống lúa Oryza sativa.L
Tiêu chuẩn này không áp dụng cho gạo nếp (glutinous rice) từ giống lúa Oryza sativa.L glutinosa và các sản phẩm được chế biến từ gạo
2. Tiêu chuẩn trích dẫn
TCVN 4733-89, Gạo yêu cầu vệ sinh
TCVN 1643:1999, Gạo-phương pháp thử
TCVN 5645:1999, Gạo-Phương pháp xác định mức xát trắng
TCVN 5646:1999, Gạo-Bao gói, ghi nhãn, bảo quản và vận chuyển
3. Yêu cầu kỹ thuật
3.1. Các chỉ tiêu cảm quan của gạo (màu sắc, mùi và vị) phải đặc trưng cho từng giống, loại gạo đó, không biến màu, không bị hư hỏng và không có mùi vị lạ.
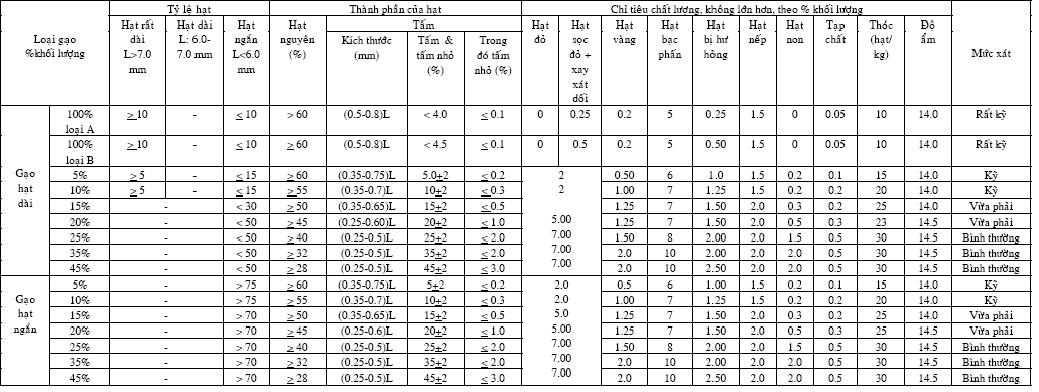
3.2. Yêu cầu về chất lượng của từng loại gạo được qui định trong bảng 1
3.3. Yêu cầu vệ sinh Theo TCVN 4733-89
4. Phương pháp thử
4.1. Các chỉ tiêu chất lượng của gạo được xác định theo TCVN 1643-1992
4.2. Mức xát trắng của gạo được xác định theo TCVN 5645:1999
5. Bao bì, ghi nhãn, bảo quản và vận chuyển: Theo TCVN 5646-1992
Bảng 1-Chỉ tiêu chất lượng của gạo trắng
It does not apply to waxy rice (Oryza sativa.L glutiniza) and products derived from this variety
3.1. Organoleptic properties of rice shall have a characteristic colour and aroma which satisfy the requirements of grades, the natural colour of rice is not changed, rice is not damaged... not having a foreign odour
3.2. Quality factors of rice are set out in Table 1
3.3. Hygienic requirements of rice shall comply with the requirements specified in TCVN 4733:1989
4.1. Determination of quality of rice shall be carried out according to TCVN 1643:1992
4.2. Determination of milling degree of rice shall be carried out according to TCVN 5645:1999